Anatomy of a guitar
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
parts of a guitar – test (your sense of humour)
Which parts of a human and guitar are the same? (answers at the end)
Anatomy of the guitar
The
Head/headstock and Tuning Keys
This part
of guitar holds the Tuning Keys, sometimes called the Machine Heads (big thumbs
up to all the Deep Purple fans). These hold the guitar strings under tension to
produce the correct pitch. There are different types of headstock. Below are
images of various headstocks
Nut
The nut
is a small raised piece of material that holds the strings off the fretboard.
It defines the scale length of the guitar. The scale length being the full
length of a vibrating string, between the bridge and the nut. A guitar nut may
be made of various materials, the most common being bone, plastic, ivory. You
may also get a locking nut which helps keep the instrument in tune,
particularly when using a Whammy Bar. These are 3 pieces of metal that hold 2
strings each, that lock using an Allen Key.
Neck/Fretboard
This is
the part of the guitar where you place your fingers to produce music through
the use of chords and single notes. On the neck, the frets indicate where your
fingers should be placed to shorten the string length, raising the pitch of
that particular string. Within the neck of modern electric guitars is a truss
rod which strengthens the neck and prevents it from distorting and helps keep
the strings in tune. Material used for
making the fretboard, again varies. Typically used would be rosewood, maple,
ebony. Hardwood material is used to prevent the guitar bursting into flame when
Eddie Van Halen or Steve Vai play!! I am not serious here, obviously I would
not recommend it but if you do want to set fire to your guitar watch Jimi
Hendrix at Monterey.
Position
markers
Guitars
have marker dots on the fretboard, these are duplicated on the side of the
guitar neck. These visual markers tell a player where different frets are on
the guitar. Imagine how hard it would be to find, let’s say, fret 11, without a
visual guide.
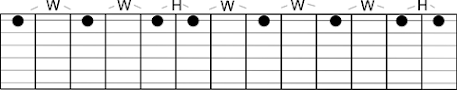
The dots
are usually marked at the 3rd, 5th, 7th, 9th
and 12th fret. The 12th fret having 2 dots to indicate an
octave above the open strings. On a 24 fret guitar, as in the picture above,
the second set of markers show the next octave above the 12th fret.
Octaves are where the notes in a scale start to repeat. Look at the symmetry of
the markers from the 12th fret outward. The fret spaces are
3,2,2,2,3. The double markers of the 12th fret also show where the
half way point on the guitar neck is, from the bridge to the nut.
Sometimes
guitars have inlays rather then dots, normally made from mother of pearl, abalone,
or a similar material. Some guitars, like a Gibson Les Paul Custom also have an
inlay on the 1st fret, they then follow the above pattern.
Another great thing about markers is when playing with another
guitarist. You can see where they are playing chords so you may play the same
chord but in a different position, or an inversion of the chord being played.
Body
Electric
guitars come with several body configurations, such as:-
Solid
Body - Hollow Body - Semi Hollow
Most electric guitar bodies are made of wood. The most common
wood used in the manufacture of electric guitar bodies are ash, maple, poplar,
alder and basswood. Most are made of two pieces of wood. The body of a solid
state guitar has to be routed during manufacture to accept the electronic
components that will produce the sound through vibration, pick-ups and
amplification.
Acoustic
guitars have gone through many changes over the years. From Renaissance and
Baroque guitars, to Classical, Flat-top, Archtop and even Dobro or Resonator
type guitars.
Acoustic
guitars produce sound through the sound hole in the guitar body. As the guitar
is hollow, the sound resonates within the body of the guitar. The wood used in
acoustic guitar manufacture tends to be spruce or cedar with the sides made
from Indian or Brazilian rosewood, or mahogany. Martin guitars, is probably the
best known acoustic guitar manufacturers. They first used strengthening within
the guitar body and also introduced the ‘dreadnought’ style of acoustic guitar.
These larger bodied acoustics gave a ‘larger’ sound. Dobro and Resonator guitar
bodies tend to be made of metal or wood. A guitar student would not really
start by learning on these instruments, so I will go into these further on
another day.
Pick
Guard
The
Pickguard, sometimes called the Scratchplate, is normally made for a thin sheet
of shaped plastic. It’s main purpose is to prevent damage to the finished
surface of the guitar. On the guitars pictured above all have a pickguard
fitted except the Ibanez (2nd from left).
Pickups/Selector
switch
Pickups are used to choose the tone of the guitar for
a particular song. The pickup chosen are selected by using the switch which
will provide a combination of tones through the pickups. The neck pickup provides
a warm tone whilst the bridge pickup gives a brighter tone. The Selector switch,
sometimes called a toggle switch, on differing guitars maybe a 3 way or a 5 way
switch. The picture below shows the combination of the selector switch for the
pickups on a 5 way switch guitar. You may also be able to set the selector
switch in a mid position between two selections this gives on out of phase sound.
Controls
The control knobs on a guitar control the volume and
tone coming from the pickups. only above picture you can see two tone control
knobs under master volume this is a Stratocaster with the middle control knob controlling
the neck pickup the lower control knob controlling the middle pickup the bridge
pickup has no tone control.
Vibrato
Bar
The Vibrato bar, also called the whammy bar, is part
of a mechanical system which temporarily changes the pitch of the strings to
create a vibrato effect. It may be also used in shred guitar playing to produce
a pitch bend often called a dive-bombing effect. Vibrato systems for guitars were
developed in the 1920s although but it became more popularly used from the 50s
onwards when guitarist like Chet Atkins and the Ventures, the Shadows and Dick
Dale used them, through the 60s and 70s guitarist like Jimi Hendrix Ritchie
Blackmore David Gilmour and more up-to-date Joe Satriani and Steve Vai have
used them.
Bridge
The bridge is a part of the guitar on the body that
supports the strings. On acoustic guitar the bridge will usually sit in the
saddle which is stuck to the body of the guitar and has a recess to accept the
bridge.
Output
Jack
A guitar lead is placed in the output chart to allow the
output signal to travel from the guitar to the amplifier therefore allowing amplified
sound through the speaker.
Strings
These come in a variety of sizes and also varying
materials eg. nylon or nickel plated steel. Nylon is used on acoustic guitars although
steel guitar strings may also be used. Electric guitars would not respond to
nylon strings, however, there are some electric acoustic models today that
employ nylon strings eg. Godin Multiac Encore Nylon Electric.
Below is a table of typical guitar string gauges. The thickness
of the string tends to indicate the tone. Last year I watched a Youtube video
where Rick Beato did a review that may dispel this theory. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wGXj_NQONYM - have a listen, you decide!
And now
the moment you have all been waiting for….
Answers –
head, neck, finger, body, nuts and hole.
Please subscribe and comment/share. Kind regards, Guitareviews4












Comments
Post a Comment